(labour costs in the EU candidate countries for 2000)
| Notation and methodological comments (labour costs in the EU candidate countries for 2000) |
| For the first time and in accordance with the Regulation 530/1999 of the European Commission, Eurostat presented in November 2002 harmonized figures for the year 2000 on labour costs for 11 of the 13 EU candidate countries. The 11 countries are |
| BG - Bulgaria |
| CY -Cyprus |
| CZ - Czech Republic |
| EE - Estonia |
| HU - Hungary |
| LT - Lithunia |
| LV - Latvia |
| PL - Poland |
| RO - Romania |
| SI - Slovenia |
| SK - Slovak Republic |
| The labour costs for these countries are broken down to different economic activities. We confine here to the the following categories (NACE Ref. 1): |
| C - Mining and quarrying |
| D - Manufacturing |
| E - Electricity, gas and water supply |
| F - Construction |
| G - Wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and personal & household goods |
| H - Hotels and restaurants |
| I - Transport, storage and communication |
| J - Financial intermediation |
| K - Real estate, renting and business activities |
| In addition, the agregates C – F (“Industry”) , G – K (“Services” ) and C – K (“Industry and Services”) are used. |
| Labour costs are total labour costs and include direct renumeration, employers’ social contributions and all other labour costs. |
| Visualization of labour costs by using bar charts and boxplots |
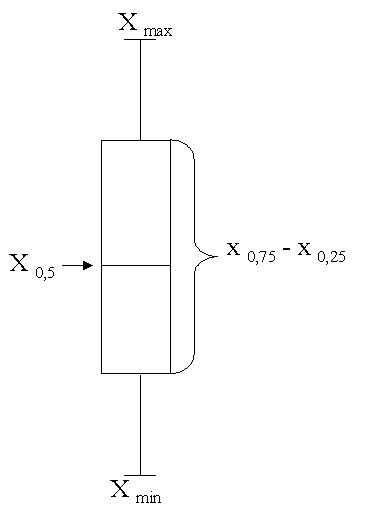
| The labour costs here are visualized by using eiher bar charts or boxplots. A bar chart is a graphical tool of descriptive Statistics which represents each element xi of the data set by means of a bar of length xi (i = 1, 2, .. ,n). A boxplot aggregates the information contained in a given data set by displaying only five characteristics of the set. It is defined by a box of length x0.75 – x0.25 (interquartile range), the median x0.5 (marked inside the box) and the two extreme values xmin and xmax of the data set. The latter are connected with the box via two lines. |
 |